Cara menggunakan pivot table merupakan keterampilan penting dalam analisis data. Dengan pivot table, Anda dapat merangkum dan menganalisis data dalam berbagai cara, dari yang sederhana hingga yang kompleks. Panduan ini akan memandu Anda langkah demi langkah dalam menguasai cara menggunakan pivot table untuk mengoptimalkan proses analisis data Anda.
Artikel ini akan membahas langkah-langkah dasar hingga lanjutan dalam menggunakan pivot table, mulai dari pengenalan hingga penggunaan fitur-fitur canggih. Anda akan mempelajari cara membuat pivot table, mengatur field, melakukan perhitungan, dan memvisualisasikan data dengan efektif. Siap untuk menguasai pivot table?
Introduction to Pivot Tables

Source: sahabatnesia.com
Pivot tables are like data superheroes! They take messy, jumbled data and turn it into crystal-clear summaries and reports. Imagine you’ve got a mountain of sales figures for your online shop – products, regions, and sales amounts, all jumbled up. Pivot tables help you slice and dice that data, showing you exactly what you need to know, like top-selling products in each region or total sales per month.
They’re super useful for anyone who needs to understand trends and patterns in their data.They’re not just for big companies; small businesses and even students can use them to make sense of data. They make data analysis way easier, helping you spot important insights that would otherwise be hidden in a sea of numbers.
Purpose of Pivot Tables
Pivot tables are designed to summarize and analyze large datasets. They allow users to reorganize and restructure data in different ways to reveal hidden patterns, trends, and relationships. This makes them incredibly useful for business intelligence, data reporting, and decision-making. They’re a powerful tool for anyone working with data.
How Pivot Tables Work
Pivot tables work by allowing you to rearrange data from rows to columns and vice versa. This reorganization lets you look at your data in different perspectives, uncovering insights you might not have seen otherwise. Think of it as a flexible table that adapts to your questions about the data. You can group data by various categories and then calculate different measures like sums, averages, counts, or percentages, depending on what you want to learn from the data.
Example Dataset
Let’s say you own a clothing store. Here’s a sample dataset you could analyze with a pivot table:
| Product | Region | Sales (Rp) |
|---|---|---|
| T-Shirt | Jakarta | 1000000 |
| Jeans | Bandung | 1500000 |
| T-Shirt | Jakarta | 1200000 |
| Dress | Surabaya | 1800000 |
| Jeans | Jakarta | 1300000 |
| Dress | Jakarta | 1400000 |
This simple table shows product, region, and sales figures. Using a pivot table, you could easily summarize total sales by product, total sales by region, or top-selling products in each region.
Types of Data Used
Pivot tables can handle various data types:
- Numerical Data: This includes quantities like sales figures, prices, and quantities. These are the numbers you use to calculate totals, averages, and other measures.
- Categorical Data: These are descriptive values like product names, colors, regions, and customer types. These are used to group and segment data.
- Date Data: Dates are useful for tracking trends over time. Pivot tables can be used to analyze sales by month, quarter, or year.
These different data types can be combined in a pivot table to gain comprehensive insights.
Basic HTML Table Structure
The sample table above can be easily transformed into a pivot table by a tool like Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel. These tools allow you to drag and drop columns and rows to reorganize the data and then calculate summaries.
Setting Up a Pivot Table
Pivot tables are like magic tools for organizing and analyzing data. Imagine sifting through a mountain of sales data—with a pivot table, you can easily find trends, outliers, and insights that would take forever to spot otherwise. It’s a game-changer for anyone working with spreadsheets, whether you’re a biz owner or just need to quickly summarize data.Pivot tables allow you to summarize and reorganize large datasets in ways that highlight patterns and trends.
They’re super flexible, letting you easily change how the data is grouped and displayed to get different perspectives.
Creating a Pivot Table in Excel
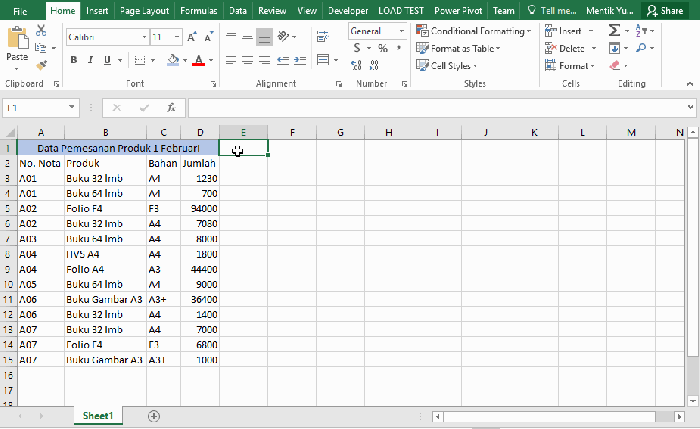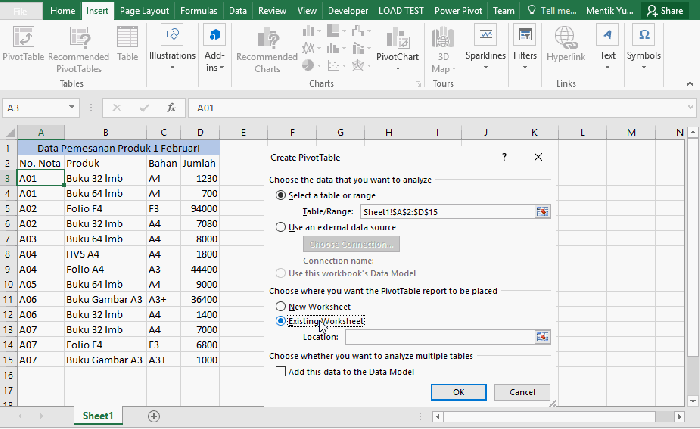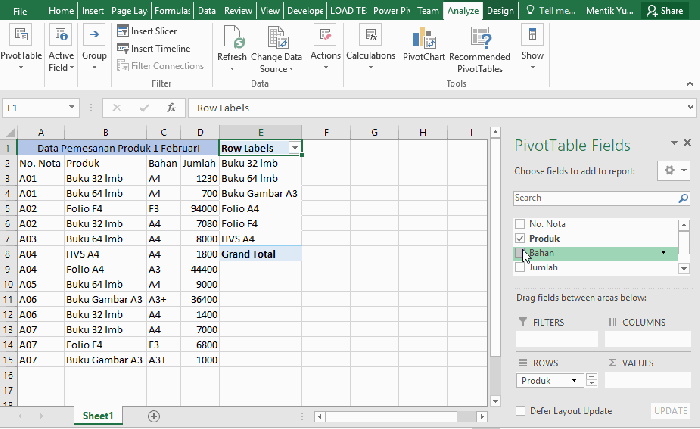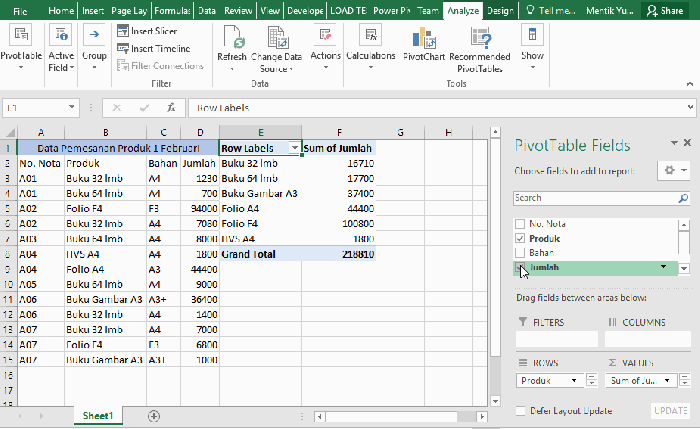
To build a pivot table in Excel, first, select the data range you want to analyze. Then, go to the “Insert” tab and click “PivotTable.” Excel will pop up a window asking where you want to put the new pivot table (a new worksheet or an existing one). Choose your spot and click “OK.”
Selecting Data for a Pivot Table
Carefully selecting the right data range is key. If you pick too little, you’ll miss crucial details; if you pick too much, you’ll end up with a huge, messy table. So, make sure your selection includes all the relevant rows and columns needed for your analysis. Think about what you want to discover from the data, and then pick the data range that covers those variables.
Pivot Table Fields
Pivot tables use “fields” to organize your data. These fields are essentially columns or rows from your original dataset. For example, if you’re analyzing sales data, “Product,” “Region,” and “Sales Amount” could all be fields. You drag these fields into different areas of the pivot table to group and summarize your data.
Data Types in Pivot Tables
You can use many different data types in pivot tables, like sales figures, customer demographics (age, location, etc.), product categories, or even dates. For instance, if you’re tracking online sales, you could use the pivot table to analyze sales by product type, by customer location, or by date ranges. This lets you explore different facets of your data, like how sales in Jakarta differ from sales in Bandung.
Steps to Create a Pivot Table (Visual Guide)
| Step | Action | Software Example (Excel) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Select the data range. | Highlight the cells containing your data. |
| 2 | Go to the “Insert” tab. | Click the “Insert” tab at the top of the Excel window. |
| 3 | Click “PivotTable.” | Find and click the “PivotTable” button in the “Tables” group. |
| 4 | Choose where to place the pivot table. | Select a new worksheet or an existing one. |
| 5 | Drag fields to rows and columns. | Drag fields like “Product,” “Region,” and “Sales Amount” to the appropriate areas in the pivot table. |
Using Pivot Table Fields

Source: webflow.com
Yo, peeps! Pivot tables are like magic, but instead of making rabbits pop out of hats, they organize your data into super-useful summaries. This part is all about how to move those fields around to get the perfect view of your data.Now, imagine you have a spreadsheet overflowing with sales figures for every product, in every region, for the whole year.
Pivot tables make it possible to quickly see trends and patterns that would take hours to spot manually. We’re gonna unlock that power by showing you how to use these fields like pro gamers.
Dragging and Dropping Fields
This is the core of using pivot tables. You drag and drop fields to control how your data is grouped and displayed. Think of it like rearranging furniture in a room – you change the layout to see things from different angles. The key is understanding where each field goes to get the desired output.
Rows, Columns, and Values Areas
- Rows: These fields determine the rows in your pivot table. For example, if you have product names, putting them in the Rows area will show the sales figures for each product separately.
- Columns: These fields determine the columns. If you want to see sales figures broken down by month, put the month field in the Columns area.
- Values: This is where you put the fields you want to summarize. If you want to see the total sales for each product, put the sales amount in the Values area. Usually, you’ll aggregate this value with functions like sum, average, or count.
Impact of Field Placement
The way you arrange fields directly affects the pivot table’s output. For instance, putting “Product” in Rows, “Region” in Columns, and “Sales Amount” in Values shows sales by product and region. Changing the order or placement will change the table, revealing different aspects of the data.
Filtering Pivot Table Data
Filtering is like zooming in on a specific part of your data. Once you’ve set up your pivot table, you’ll find filter options. Clicking these allows you to show only certain product types, regions, or periods. This makes it easy to pinpoint important trends and exceptions.
Sorting Data Within a Pivot Table
Sorting lets you arrange your data in ascending or descending order. Imagine you want to see the top-selling products. You can sort the “Sales Amount” column in descending order to easily identify the top performers. This is a great way to find patterns in your data and understand how things are trending.
Aggregating Data, Cara menggunakan pivot table
- Sum: Used to add up values. Great for calculating total sales.
- Average: Calculates the mean. Useful for finding the average sales per product.
- Count: Counts the number of items. Perfect for knowing how many sales were made for a particular product.
Here’s a table illustrating the effect of field placements:
| Field in Rows | Field in Columns | Field in Values | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product | Region | Sales Amount | A breakdown of total sales for each product in each region. |
| Region | Product | Sales Amount | A breakdown of total sales for each region by product. |
| Month | Product | Sales Amount | A breakdown of total sales for each product in each month. |
This table clearly shows how rearranging the fields changes the summarized data. You’ll get different insights depending on how you position your data. That’s the power of pivot tables – flexibility in exploring your data.
Common Pivot Table Calculations
Source: advernesia.com
Pivot tables are super useful for quickly analyzing data and finding hidden patterns. Imagine you’ve got a ton of sales data – with pivot tables, you can easily see which products are selling the most, which regions are performing best, and even spot trends over time. It’s like having a superpower for data!
Performing Calculations
Pivot tables let you do more than just display data. You can calculate sums, averages, counts, and percentages directly within the table. This makes it super easy to get insights and answer important business questions without needing separate calculations. For example, you can instantly see the total revenue for each product category or the average sales per region.
- Sums: To find the total sales for each product, just drag the sales column into the Values area of the pivot table. Pivot tables automatically sum up the values for you.
- Averages: To see the average sales for each region, change the summarization method from Sum to Average in the Values area settings. This shows you the average sales performance across different regions.
- Counts: To see how many sales records exist for each product, change the summarization method to Count. This is handy for knowing how frequently a product is being sold.
- Percentages: You can calculate percentages by using the % option in the Values area, which automatically calculates the percentage of the total for each value. For example, you could calculate the percentage of total sales coming from each region.
Grouping Data
Grouping data in pivot tables is key to understanding trends. You can group your data by various criteria, like month, region, or product category, to see how these factors affect your metrics.
- By Month: If you have sales data for each month, you can group the data by month to see sales trends over time. This will show you how sales change over the course of the year.
- By Region: You can group sales data by region to analyze performance in different geographical areas. This allows you to see which regions are performing well and which ones might need more attention.
Calculating Totals and Subtotals
Pivot tables automatically calculate totals, subtotals, and grand totals based on the grouping and summarization you’ve selected.
- Totals: These show the sum or average for each group. For example, you can see the total sales for each product category.
- Subtotals: These break down totals further. For instance, you could see the total sales for each product within each region.
- Grand Totals: This is the overall sum or average for all the data. For example, you can see the grand total sales across all products and regions.
Creating Calculated Fields
You can create custom calculations within pivot tables. This is useful when you need to perform more complex analysis, like calculating profit margins or finding the difference between sales and costs.
- Custom Calculations: Calculated fields in pivot tables allow you to perform calculations on existing data to create new metrics. For example, you can create a calculated field to calculate profit margin by subtracting cost from sales.
Analyzing Trends and Patterns
Pivot tables are incredibly helpful for identifying trends and patterns in your data. By grouping and summarizing data in different ways, you can quickly spot upward or downward trends, seasonal fluctuations, and other important insights.
| Metric | Calculation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Total Sales | Sum of Sales | Total revenue generated by all products |
| Average Sales per Product | Average of Sales | Average revenue generated by each product type |
| Sales Growth Rate (Month-over-Month) | Percentage change in sales from one month to the next | Calculate how much sales have increased or decreased between consecutive months |
Advanced Pivot Table Features
Pivot tables, while powerful for basic analysis, unlock even more awesomeness with advanced features. Imagine digging deeper into your data, visualizing trends, and finding hidden patterns – that’s the magic of these advanced tricks. Let’s level up your pivot table game!
Pivot Charts for Visualizations
Pivot tables aren’t just about numbers; they’re about insights. Pivot charts transform your numerical data into visually appealing graphs and charts, making it super easy to spot trends, outliers, and overall patterns. This visual representation can make complex data much easier to understand, turning raw figures into compelling stories.
Custom Calculations in Pivot Tables
Sometimes, the built-in calculations aren’t quite enough. Creating custom calculations allows you to tailor the analysis to your specific needs. You can add new measures, perform complex calculations, or even build formulas that aggregate data in ways that standard functions don’t support. This gives you the flexibility to analyze data from unique perspectives. For example, you can calculate the percentage change of sales compared to the previous period.
Slicers for Interactive Filtering
Slicers are like interactive filters for your pivot tables. They let you slice and dice your data with ease, enabling dynamic exploration. With a few clicks, you can isolate specific subsets of your data, instantly filtering the pivot table results based on criteria you choose. Imagine being able to see sales figures just for specific product categories or regions – slicers make that possible.
Identifying Outliers and Anomalies
Pivot tables can be used to spot anomalies and outliers in your data. By examining aggregated data across various dimensions, you can identify trends that deviate significantly from the norm. These insights can help you understand the factors behind unexpected results, or perhaps, pinpoint errors in your data collection. For example, if you see a sudden drop in sales for a particular product, you can use pivot tables to analyze the underlying reasons.
Creating Multiple Pivot Tables
From a single dataset, you can create multiple pivot tables. This allows for different perspectives and analyses of the same data. Imagine creating one table to see sales by region and another to see sales by product category. This lets you examine the data from various angles, uncovering hidden correlations and gaining a deeper understanding.
Practical Example: Advanced Pivot Table Features
| Product | Region | Sales | Profit Margin | Quantity Sold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laptop | North | $10,000 | 25% | 50 |
| Laptop | South | $12,000 | 20% | 60 |
| Tablet | North | $5,000 | 30% | 25 |
| Tablet | South | $6,000 | 25% | 30 |
Using this dataset, you could:
- Create a pivot chart visualizing sales trends by region for each product.
- Calculate a custom field for the “Total Revenue” by multiplying “Sales” and “Quantity Sold”.
- Add a slicer to filter the table by product type, allowing users to quickly see sales figures for laptops or tablets.
- Identify potential outliers in profit margins by using pivot table calculations to highlight significant deviations.
- Create separate pivot tables to analyze sales by region and profit margins separately.
Pivot Tables in Different Applications
Pivot tables are seriously game-changers for organizing and analyzing data. They’re like magic spreadsheets, letting you slice and dice your info in ways you never thought possible. Imagine quickly finding trends, spotting outliers, and making smarter decisions – all with just a few clicks. But the cool thing is, pivot tables aren’t limited to one software program; they’re everywhere!Pivot tables are a powerful tool for data analysis across various software platforms.
They allow users to summarize and analyze large datasets efficiently, providing insights into trends and patterns. This versatility makes them indispensable for data-driven decision-making in diverse fields.
Pivot Tables in Excel
Excel is the OG of spreadsheet software, and its pivot tables are legendary. They’re super intuitive and offer a ton of customization options. Imagine having a massive sales dataset – with pivot tables, you can quickly group sales by region, product, or time period, and see total sales for each category. It’s like having a crystal ball for your business data.
- Setting up a Pivot Table in Excel: Select the data range, go to the “Insert” tab, and click “PivotTable.” Excel will create a new sheet with a pivot table field list. Drag the fields you want to analyze into the appropriate areas (Rows, Columns, Values). Adjusting filters and calculations are also straightforward.
- Example: Analyzing sales data. Drag “Region” to Rows, “Product” to Columns, and “Sales Amount” to Values. Excel will automatically calculate total sales for each product in each region. You can then further filter by date or other criteria.
Pivot Tables in Google Sheets
Google Sheets, the cloud-based spreadsheet powerhouse, also rocks pivot tables. They’re essentially the same as Excel’s, but with the added convenience of being accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. The basic functionalities are very similar to Excel.
- Setting up a Pivot Table in Google Sheets: Select your data, click “Insert,” then “Pivot table.” You’ll get a new sheet with a pivot table field list. Drag and drop fields to Rows, Columns, and Values just like in Excel.
- Example: Analyzing website traffic data. Drag “Date” to Rows, “Source” to Columns, and “Page Views” to Values. Google Sheets will instantly display page views for different sources over time. You can filter by specific dates, devices, or other attributes.
Pivot Tables in Other Spreadsheet Programs
Other spreadsheet programs, like LibreOffice Calc and Apple Numbers, have pivot tables as well. Their functionality is similar to Excel and Google Sheets, but might have slight differences in the interface and features. They are helpful for organizing data from various sources into a manageable format for analysis.
- Key Differences: While the core concepts remain the same, the exact layout and available options might differ slightly. Explore the help menus for specific features.
- Example: Analyzing financial statements in LibreOffice Calc. You can group data by different expense categories and view the total for each category.
Comparison of Pivot Table Functionalities
| Feature | Excel | Google Sheets | LibreOffice Calc | Apple Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Local files, cloud services | Cloud services, local files | Local files, cloud services | Local files, cloud services |
| Customization | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive | Extensive |
| Calculations | Various aggregate functions | Various aggregate functions | Various aggregate functions | Various aggregate functions |
| Collaboration | Limited to file sharing | Built-in collaboration | Limited to file sharing | Limited to file sharing |
Real-World Applications of Pivot Tables: Cara Menggunakan Pivot Table
Pivot tables are seriously game-changers for any business. Imagine having all your data neatly organized, ready to be sliced and diced for insights that unlock hidden opportunities and help you make better decisions, like a boss! They’re not just for nerds; anyone who needs to understand trends and patterns in their data can use them.Pivot tables are incredibly versatile tools that can be used across various industries.
They help businesses transform raw data into actionable information, which is key to making informed decisions. From figuring out sales trends to spotting marketing weaknesses, pivot tables are the secret weapon of data-driven decision-making.
Pivot Tables in Sales
Sales teams use pivot tables to analyze sales performance, identify top-performing products or regions, and spot trends. They can quickly see sales figures by product, by region, by salesperson, and even by time period. This lets them understand what’s working, what’s not, and adjust strategies for better results. For example, a sales team could use a pivot table to see that sales of widgets are booming in the Southeast region, while sales of gadgets are struggling in the Northeast.
This kind of quick insight can help them focus their efforts on the regions and products that are performing best.
Pivot Tables in Marketing
Marketers use pivot tables to analyze customer data, track campaign performance, and understand customer behavior. They can see how different marketing channels are performing, what campaigns are generating the most leads, and which demographics are most responsive to specific marketing efforts. For example, a marketing team might use a pivot table to discover that social media ads are driving a lot of traffic to their website, while email campaigns are not performing as well.
This lets them adjust their marketing budget and strategies.
Pivot Tables in Finance
Financial analysts use pivot tables to analyze financial statements, track budgets, and identify areas of concern. They can see financial data by category, by time period, and by other criteria. This helps them monitor expenses, revenue, and profitability, and to spot potential financial risks. For instance, a financial analyst might use a pivot table to pinpoint that operating costs are rising faster than expected in the Q3.
This allows for proactive measures to be taken to control these rising costs.
Case Study: A Retail Store’s Pivot Table Success
Imagine a retail store that sells clothing. They’re struggling to understand sales trends and need to identify which products are selling well and which aren’t. They use a pivot table to analyze sales data by product category, price range, and customer demographics. The pivot table reveals that while high-end clothing is selling very well, the mid-range clothing isn’t selling as much as expected.
This crucial insight helps the store adjust inventory levels, and re-evaluate their pricing strategy.
Best Practices for Using Pivot Tables
Pivot tables are like magic wands for data – they help you transform messy spreadsheets into crystal-clear insights. But to wield this power effectively, you gotta follow some best practices. Knowing these tricks will save you time and frustration, plus you’ll get way better results.Using pivot tables effectively involves more than just dragging fields around. It’s about understanding how to optimize your data for maximum insight.
This includes meticulous data preparation, intelligent labeling, and careful validation to ensure your results are accurate and reliable. Let’s dive into the key practices.
Creating Efficient and Effective Pivot Tables
Pivot tables are super helpful, but they can get overwhelming if you don’t design them right. A well-structured pivot table is a clear, concise summary of your data, allowing you to quickly spot trends and patterns. Efficiency is key. To create efficient pivot tables, start with a clear understanding of what you want to analyze. Identify the key metrics, dimensions, and relationships in your data.
- Start with a clean dataset. If your data has errors, inconsistencies, or missing values, it will affect the accuracy of your pivot table results.
- Choose the right fields for your analysis. Don’t just randomly drag fields into the table. Consider which fields will give you the most insightful results.
- Use calculated fields when necessary. Pivot tables can perform basic calculations, but you can also create custom calculations for more complex analyses.
Importance of Clear Labeling and Formatting
Clear labeling is crucial for understanding your pivot table. Imagine a pivot table with cryptic abbreviations – it’s like trying to decipher a secret code! Clear labels help everyone, especially if you’re sharing the pivot table with others. Consistent formatting further enhances readability.
- Use descriptive labels for all fields and columns. Instead of “Sales Q1,” use “Sales Figures – Q1 2024”.
- Apply consistent formatting to make the table visually appealing and easy to scan. Use colors, fonts, and other formatting elements to highlight key information.
- Include a clear title and a brief description explaining the purpose of the pivot table.
Data Cleaning and Preparation Before Creating a Pivot Table
Garbage in, garbage out – this saying holds true for pivot tables. Before you even start dragging and dropping, ensure your data is clean. Dirty data leads to inaccurate results, and that’s no good. Prepare your data by handling missing values, inconsistencies, and outliers.
- Identify and handle missing values. Decide whether to remove rows with missing values, fill them with averages, or use other appropriate methods.
- Correct any data entry errors. This might involve fixing typos, ensuring consistent formats, or validating data ranges.
- Standardize data formats. Ensure that all relevant fields use the same format, like dates or currency.
Significance of Data Validation and Accuracy
Data accuracy is paramount. If your data is wrong, your pivot table results will be wrong too. Use validation rules to check your data for errors and inconsistencies before you start analyzing it. Ensuring accuracy will prevent costly mistakes.
- Validate data types. Make sure that your data fields are correctly categorized as numbers, text, or dates.
- Implement data validation rules to ensure data integrity. This might involve specifying the valid values or ranges for certain fields.
- Cross-reference your data with other sources to verify its accuracy.
Step-by-Step Guide for Designing Effective Pivot Tables
A well-designed pivot table is like a well-organized library. It makes finding specific information easy and efficient. Here’s a guide to creating one.
- Understand your data: First, examine the data to understand the variables and relationships within it.
- Choose the right fields: Select the fields you want to analyze and group your data by.
- Configure the pivot table: Drag and drop the fields into the appropriate areas of the pivot table (rows, columns, values). Think carefully about how to group your data to see the relationships.
- Validate the results: Check the results for any obvious errors or inconsistencies. Look for unusual patterns or unexpected values. Compare your findings to other data sources or business knowledge.
- Iterate and refine: If needed, adjust your pivot table design, add calculated fields, or filter your data to get more specific insights.
Pivot Table Limitations
Pivot tables are super useful for summarizing and analyzing data, but they ain’t a magic bullet. They have some limitations that you gotta be aware of to avoid getting misled. Understanding these limitations helps you pick the right tool for the job, whether it’s a pivot table or something more advanced.
Limitations in Handling Complex Relationships
Pivot tables excel at summarizing data, but they struggle with complex relationships between different variables. If your analysis needs to account for intricate cause-and-effect connections, you might need a more advanced statistical modeling technique. For example, if you’re trying to figure out how marketing spend affects sales, but also need to factor in seasonality and competitor activity, a pivot table alone won’t cut it.
You’d likely need something like regression analysis.
Inability to Perform Predictive Modeling
Pivot tables are great for descriptive analysis, but they can’t do predictive modeling. If you want to forecast future trends or predict outcomes based on historical data, pivot tables are not the right choice. Techniques like time series analysis, machine learning algorithms, or statistical modeling are better suited for such tasks.
Data Complexity and Volume
For massive datasets, pivot tables can become sluggish and slow. Imagine a dataset with millions of rows. Trying to create a pivot table that handles that volume effectively can take a long time, even with a powerful computer. If you’re dealing with data at that scale, more sophisticated tools like data warehouses or cloud-based analytical platforms are more efficient.
Limited Statistical Analysis
Pivot tables offer basic calculations like sums, averages, and counts. If your analysis requires more advanced statistical tests or measures, such as hypothesis testing, correlation analysis, or variance analysis, you’ll need a dedicated statistical software package or programming language.
Comparison with Alternative Methods
| Feature | Pivot Tables | Statistical Modeling | Machine Learning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data summarization | Excellent | Good, but often requires preparation | Less direct, often needs specific modeling |
| Complex relationships | Limited | Excellent | Excellent |
| Predictive modeling | Not applicable | Often applicable | Excellent |
| Data volume | Can be slow with large datasets | Usually more efficient | Often more efficient |
| Statistical analysis | Basic | Extensive | Extensive |
Understanding these limitations is crucial. Choosing the right tool for the job—whether it’s a pivot table or a more sophisticated analytical technique—ensures accurate and meaningful insights from your data.
Final Review
Semoga panduan ini membantu Anda memahami cara menggunakan pivot table dengan lebih baik. Dari langkah awal hingga fitur-fitur lanjutan, Anda telah mempelajari berbagai teknik untuk menganalisis dan memvisualisasikan data. Ingatlah untuk selalu berlatih dan bereksperimen dengan data Anda sendiri untuk mengasah keterampilan Anda dalam menggunakan pivot table.